Discovery and Occurrence
- Discovered in 1751 in Stockholm, Sweden by A.F. Cronstedt from the ore kupfernickel (niccolite).
- Mainly occurs in arsenic and sulfide ores.
- Extracted by roasting to NiO and then reducing with carbon.
- Abundance of 80 ppm in the Earth’s crust.
Properties
- Silver-white metal.
- Hard, malleable, and ductile.
- Ferromagnetic up to 360 °C.
- Fair electrical conductivity (25% that of copper) and heat conductivity.
- Belongs to the iron-cobalt group of metals.
- Highly resistant to atmospheric corrosion.
- Resists most acids but is attacked by oxidizing acids like nitric acid.
Isotopes
- Natural nickel is a mixture of five stable isotopes.
- Nine unstable isotopes are known.
Toxicity
- Nickel carbonyl is highly toxic, and exposure should be limited.
- Fumes and dust of nickel sulfide are recognized as having carcinogenic potential.
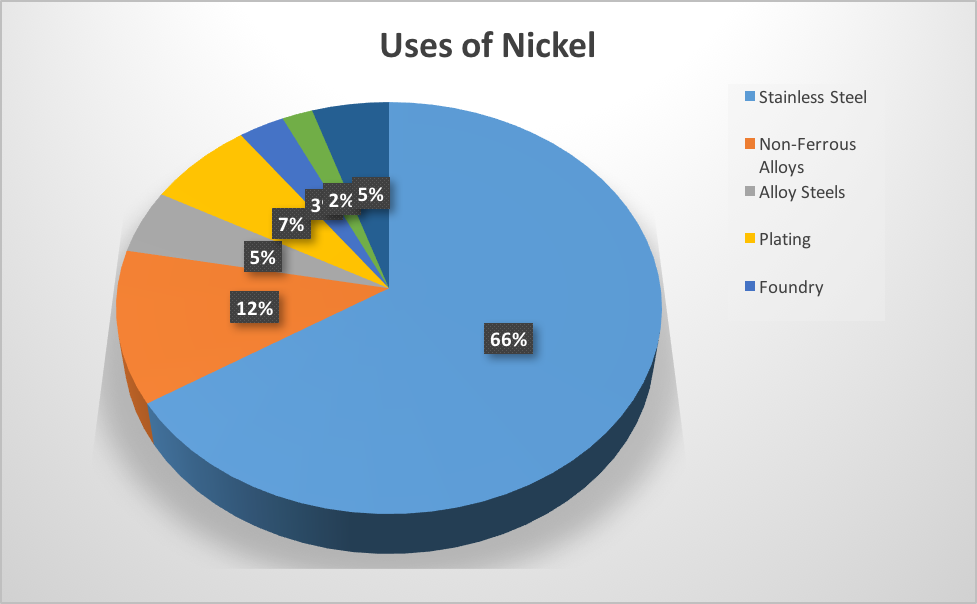
Applications
- Alloys
- Principal use as an alloying element in stainless steels, alloy steels, non-ferrous metals, and corrosion-resistant alloys (e.g., Invar, Monel, Inconel, Nichrome, Permalloy, Hastelloys).
- Coatings
- Nickel coatings can be deposited electrolytically by electroplating or chemically by electroless deposition.
- Desalination
- Tubing for desalination plants.
- Coinage
- Used in coinage.
- Armour and Vault Metals
- Added to armour plate and burglarproof vault metals.
- Glass
- Used in glass to produce a green color.
- Catalyst
- Used as a catalyst for hydrogenating vegetable oils.
- Ceramics
- Used in ceramic manufacturing.
- Magnets
- Used in Alnico magnets.
- Batteries
- Used in storage batteries, such as nickel-cadmium and nickel-metal hydride batteries, used in mobile phones and personal stereo equipment.
- High Purity Applications
- High-purity nickels are used in electronic and aerospace applications, chemical and food processing equipment, anodes and cathodes, caustics evaporators, and heat shields.
- Aerospace
- Used in aircraft turbines components.
- Beryllium Nickel
- Used for springs, switches, bellows, diaphragms, and small valves.
- Temperature Measurement
- Used in thermometer bulbs and resistance thermometers.
- Seals
- Used in glass-to-metal and ceramic-to-metal seals.
- Industrial Equipment
- Used in marine, petroleum, and chemical processing equipment (e.g., Monels).
- Incineration
- Used in incineration systems.
- Superalloys
- Used in controlled expansion nickel superalloys.
- Paramagnetic Alloys and Shape Memory Alloys
- Used in various applications such as fire-sprinkler actuators, tap water anti-scalding devices, green house window hinges, flow regulators, spacecraft solar-panel releases, toys, and underwire brassieres.





ilwxfs
Абсолютно свежие новости индустрии.
Все мероприятия самых влиятельных подуимов.
Модные дома, бренды, haute couture.
Самое лучшее место для стильныех хайпбистов.
https://fashionvipclub.ru/
Очень свежие новости мировых подиумов.
Актуальные эвенты известнейших подуимов.
Модные дома, торговые марки, haute couture.
Интересное место для стильныех хайпбистов.
https://sneakero.ru/
Самые стильные новинки модного мира.
Все новости известнейших подуимов.
Модные дома, торговые марки, haute couture.
Приятное место для трендовых хайпбистов.
https://sneakersgo.ru/
Actual wristwatch news and events. Fresh collections, models. Up to date information about famous watch companies.
https://chrono.luxepodium.com/
Точно свежие новости мировых подиумов.
Актуальные события известнейших подуимов.
Модные дома, бренды, haute couture.
Самое лучшее место для стильныех хайпбистов.
https://ulmoda.ru/
Несомненно свежие новости моды.
Исчерпывающие мероприятия лучших подуимов.
Модные дома, лейблы, гедонизм.
Новое место для стильныех хайпбистов.
https://paris.luxepodium.com/
Самые важные события модного мира.
Актуальные мероприятия известнейших подуимов.
Модные дома, бренды, высокая мода.
Самое лучшее место для стильныех людей.
https://luxury.superpodium.com/
Style, luxury, lifestyle
Perfect fashion portal for hypebeasts and cute people.
Style news, events. Last collections, collaborations, limited editions.
https://dubai.luxepodium.com/
Style, luxe, lifestyle
Perfect style startpage for hypebeasts and cute people.
Fashion news, events. New collections, collaborations, drops.
https://london.luxepodium.com/
Несомненно свежие новинки мировых подиумов.
Актуальные события всемирных подуимов.
Модные дома, лейблы, высокая мода.
Самое лучшее место для трендовых людей.
https://richlifestyle.ru/
Style, luxury, travel
The best fashion home for hypebeasts and stylish people.
Style news, events. Latest collections, collaborations, drops.
https://lepodium.in/
Избранные актуальные новости часового мира – свежие модели культовых часовых брендов.
Точно все коллекции хронографов от недорогих до экстра роскошных.
https://podium24.ru/
Наиболее трендовые новости мировых подиумов.
Актуальные эвенты лучших подуимов.
Модные дома, лейблы, гедонизм.
Интересное место для трендовых хайпбистов.
https://furluxury.ru/
Точно стильные новинки мира fashion.
Актуальные эвенты лучших подуимов.
Модные дома, торговые марки, гедонизм.
Интересное место для стильныех людей.
https://fe-style.ru/
Наиболее актуальные новости модного мира.
Все мероприятия мировых подуимов.
Модные дома, лейблы, гедонизм.
Свежее место для модных хайпбистов.
https://balenciager.ru/
Наиболее актуальные новости мира fashion.
Актуальные эвенты самых влиятельных подуимов.
Модные дома, торговые марки, высокая мода.
Самое приятное место для стильныех людей.
https://outstreet.ru/
Все свежие события мира часов – свежие модели именитых часовых брендов.
Точно все коллекции часов от доступных до очень роскошных.
https://bitwatch.ru/
Абсолютно стильные новинки индустрии.
Важные события лучших подуимов.
Модные дома, торговые марки, гедонизм.
Самое лучшее место для стильныех хайпбистов.
https://luxe-moda.ru/
LeCoupon: интересные новинки для любителей fashion шоппинга
Лента новостей, события, актуальные образы, эвенты, дропы, показы.
https://qrmoda.ru/
LeCoupon: интересные события для любителей fashion шоппинга
Лента новостей, события, актуальные образы, мероприятия, коллекции, показы.
https://qrmoda.ru/
Полностью свежие новинки индустрии.
Актуальные мероприятия мировых подуимов.
Модные дома, бренды, гедонизм.
Приятное место для модных хайпбистов.
https://egomoda.ru/
Несомненно важные события мира fashion.
Исчерпывающие события известнейших подуимов.
Модные дома, торговые марки, высокая мода.
Самое лучшее место для стильныех хайпбистов.
https://fashion5.ru/
Несомненно важные события мира fashion.
Актуальные эвенты мировых подуимов.
Модные дома, торговые марки, haute couture.
Приятное место для модных людей.
https://rfsneakers.ru
Очень важные новости индустрии.
Важные события всемирных подуимов.
Модные дома, торговые марки, высокая мода.
Самое лучшее место для модных хайпбистов.
https://whitesneaker.ru/
Очень важные новинки моды.
Важные эвенты всемирных подуимов.
Модные дома, лейблы, haute couture.
Лучшее место для трендовых хайпбистов.
https://modavmode.ru
Несомненно важные новости мира fashion.
Все новости мировых подуимов.
Модные дома, торговые марки, haute couture.
Самое лучшее место для стильныех людей.
https://urban-moda.ru/
Полностью стильные новости моды.
Абсолютно все мероприятия известнейших подуимов.
Модные дома, бренды, высокая мода.
Самое лучшее место для трендовых людей.
https://miramoda.ru
Очень свежие новинки мировых подиумов.
Все события мировых подуимов.
Модные дома, торговые марки, haute couture.
Самое приятное место для модных хайпбистов.
https://sofiamoda.ru
Очень актуальные события мира fashion.
Важные эвенты мировых подуимов.
Модные дома, торговые марки, высокая мода.
Интересное место для трендовых хайпбистов.
https://worldsfashion.ru/
Очень важные новинки мира fashion.
Актуальные мероприятия всемирных подуимов.
Модные дома, торговые марки, haute couture.
Лучшее место для стильныех хайпбистов.
https://fashionsecret.ru
Очень важные новинки модного мира.
Важные события всемирных подуимов.
Модные дома, лейблы, haute couture.
Самое приятное место для трендовых людей.
https://fashionablelook.ru
Полностью трендовые новости подиума.
Исчерпывающие эвенты лучших подуимов.
Модные дома, лейблы, haute couture.
Приятное место для стильныех хайпбистов.
https://modavgorode.ru
Самые свежие новости подиума.
Все новости лучших подуимов.
Модные дома, лейблы, гедонизм.
Самое приятное место для модных хайпбистов.
https://myfashionacademy.ru/
Наиболее актуальные новости модного мира.
Актуальные эвенты лучших подуимов.
Модные дома, торговые марки, высокая мода.
Новое место для стильныех людей.
https://modaizkomoda.ru
Точно актуальные новинки модного мира.
Важные эвенты самых влиятельных подуимов.
Модные дома, лейблы, haute couture.
Свежее место для стильных хайпбистов.
https://metamoda.ru/moda/599-doja-cat-vyzvala-bezumie-v-tope-i-yubke-iz-pishchevoy-plenki-s-rezhisserom-vetements-guram-gvasalia/
Полностью важные новости моды.
Актуальные события самых влиятельных подуимов.
Модные дома, лейблы, высокая мода.
Новое место для трендовых хайпбистов.
https://metamoda.ru/moda/599-doja-cat-vyzvala-bezumie-v-tope-i-yubke-iz-pishchevoy-plenki-s-rezhisserom-vetements-guram-gvasalia/